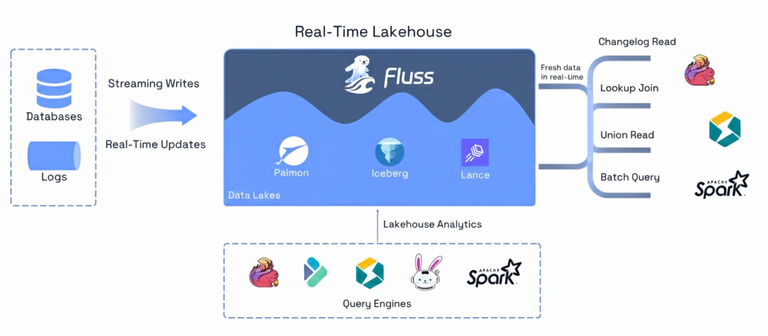
As software and data engineers, we've witnessed Apache Iceberg revolutionize analytical data lakes with ACID transactions, time travel, and schema evolution. Yet when we try to push Iceberg into real-time workloads such as sub-second streaming queries, high-frequency CDC updates, and primary key semantics, we hit fundamental architectural walls. This blog explores how Fluss × Iceberg integration works and delivers a true real-time lakehouse.
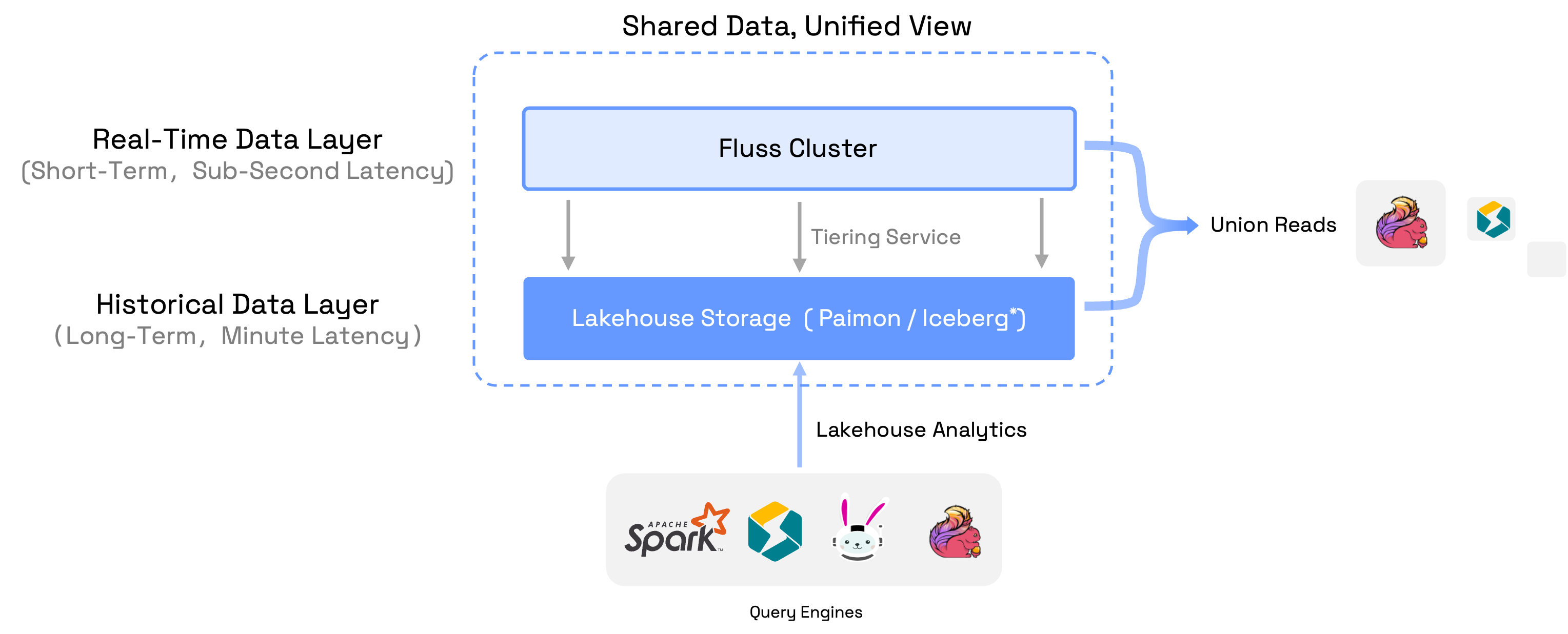
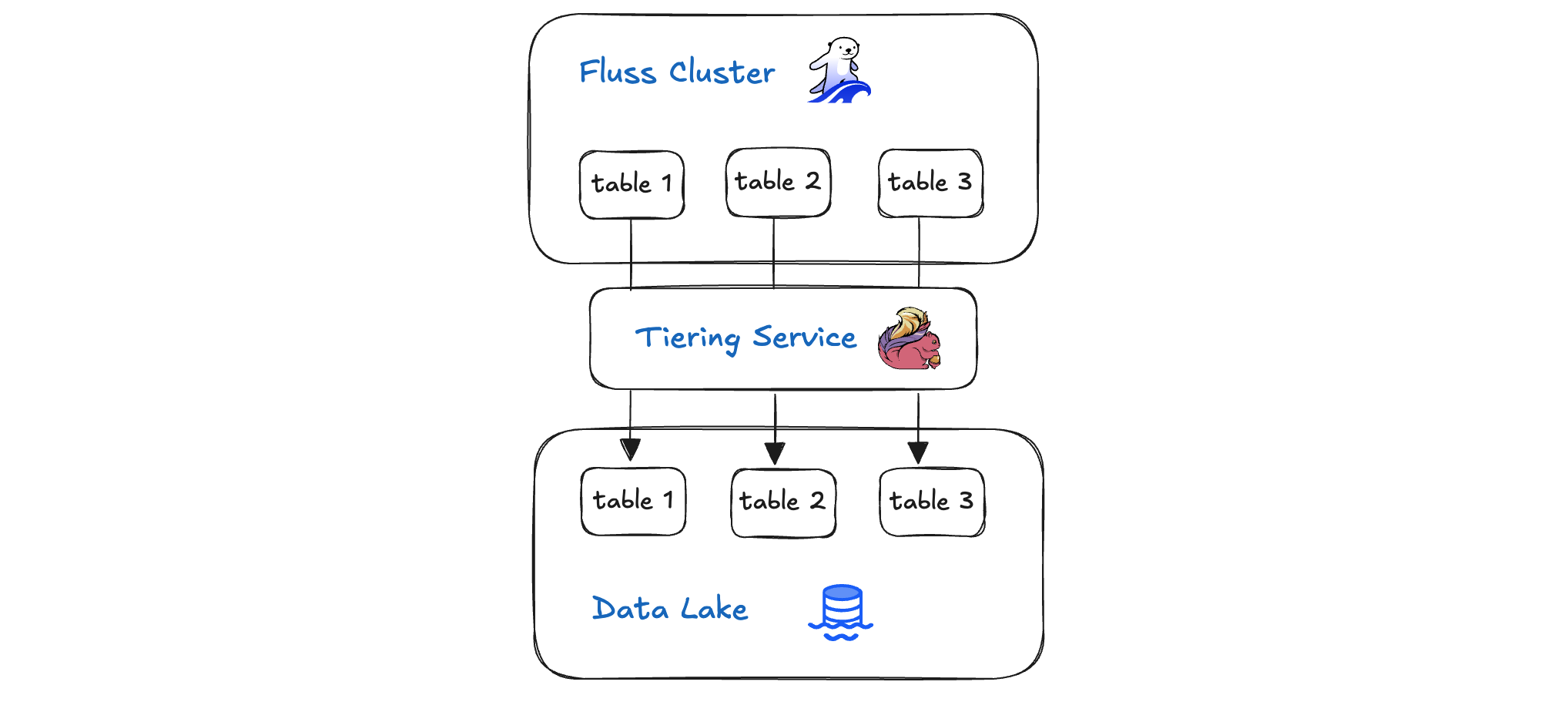
Apache Fluss represents a new architectural approach: the Streamhouse for real-time lakehouses. Instead of stitching together separate streaming and batch systems, the Streamhouse unifies them under a single architecture. In this model, Apache Iceberg continues to serve exactly the role it was designed for: a highly efficient, scalable cold storage layer for analytics, while Fluss fills the missing piece: a hot streaming storage layer with sub-second latency, columnar storage, and built-in primary-key semantics.
After working on Fluss–Iceberg lakehouse integration and deploying this architecture at a massive scale, including Alibaba's 3 PB production deployment processing 40 GB/s, we're ready to share the architectural lessons learned. Specifically, why existing systems fall short, how Fluss and Iceberg naturally complement each other, and what this means for finally building true real-time lakehouses.